Health Science | National Health Science Assessment | NCHSE | National Health Science Standards
What Are the National Health Science Standards?
With past experience in teaching, a couple of degrees in writing, and an upbringing immersed in medical jargon, Mike is positioned well to hear out the most common questions teachers ask about the iCEV curriculum. His goal is to write content that quickly and effectively answers these questions so you can back to what matters - teaching your students.
Are you new to teaching CTE health science classes? If so, you’re probably looking for direction on what topics to teach and how to organize your syllabus.
In our experience working with health science instructors like you, many teachers tell us that they use the National Consortium for Health Science Education (NCHSE) National Health Science Standards as a starting point when planning their course curriculum.
In this article, you’ll learn why NCHSE created the standards, what the standards entail, and how to teach a curriculum based on the National Health Science Standards.
You’ll also learn how the AES digital curriculum aligns with the NCHSE National Health Science Standards and prepares students for the National Health Science Assessment.
What’s the Purpose of the National Health Science Standards?
NCHSE is a partnership of educators, professionals, and organizations focused on improving health science education across the United States with industry sectors’ common standards.
There are eleven common healthcare foundation standards within four career pathways: Diagnostic, Therapeutic, Environmental, and Health Information for employers, teachers, instructors, and professional organizations to follow when educating.
The NHSS are divided into 11 Foundation Standards:
- Academic Foundation
- Communications
- Systems
- Employability Skills
- Legal Responsibilities
- Ethics
- Safety Practices
- Teamwork
- Health Maintenance Practices
- Technical Skills
- Information Technology in Healthcare
Each of these standards is broken down into specific sub-categories related to skills and knowledge all healthcare workers should have before entering the workforce.
These standards are often reviewed and updated to stay up-to-date with current trends in the industry.
In August 2022, the newest edition of the National Health Science Standards was announced with minor changes from the previous version.
When used in a curriculum, the National Health Science Standards can prepare your students to take the National Health Science Assessment - an exam developed by NCHSE to measure a student’s knowledge of health science skills and concepts.
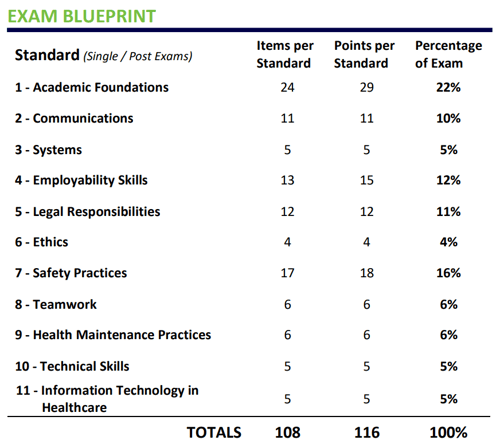
The National Health Science Assessment (NHSA) is administered by Precision Exams — a well-known industry certification provider — via an online portal. In terms of structure, the exam is made up of 108 test items that add up to a total of 116 points.
While it’s important to note that the National Health Science Assessment certificate is not a right-to-work credential or accredited certification, it is the perfect way for high school students to show that they are ready to take the next step on the path towards becoming healthcare professionals!
Read More: Help Your Students Succeed on the National Health Science Assessment
Now let’s dive into each standard and their subcategories:
Standard 1: Academic Foundation
The purpose of the Academic Foundation Standard is for students to understand human anatomy, physiology, common diseases and disorders, and medical math principles.
There are three sub-categories in the Academic Foundation Standard:
- 1.1 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Objectives for students to describe the human body’s organization and directional terms.
- 1.2 Diseases and Disorders - Objectives include students describing etiology, pathology, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of common diseases and disorders. Students should also describe biomedical therapies related to the prevention, pathology, and treatment of disease.
- 1.3 Medical Mathematics - Objectives include students demonstrating competency using basic math skills and mathematical conversions as they relate to healthcare.
Standard 2: Communications
The purpose of the Communications Standard is for students to demonstrate secure and professional delivery methods and obtain information while communicating effectively.
There are three sub-categories in this standard:
- 2.1 Concepts of Effective Communication - Objectives include students modeling verbal and nonverbal therapeutic communication.
- 2.2 Medical Terminology - Objectives include interpreting common medical abbreviations and communicating information.
- 2.3 Written Communication Skills - Objectives include using proper written and electronic communication elements and demonstrating appropriate use of digital communication in a work environment, such as email, text, and social media.
Standard 3: Systems
The purpose of the Systems Standard is for students to identify how critical systems affect services performed and quality of care.
There is one sub-category in this standard:
- 3.1 Healthcare Delivery Systems - Objectives include students differentiating healthcare delivery systems and healthcare-related agencies.
Standard 4: Employability Skills
The purpose of the Employability Skills Standard is for students to use employability skills to enhance employment opportunities and job satisfaction.
There are four sub-categories in the Employability Skills standard:
- 4.1 Personal Traits of the Health Professional - Objectives include the ability to identify personal traits and attitudes desirable in a health team’s career-ready member.
- 4.2 Employability Skills - Objectives include students’ ability to apply employability skills in healthcare.
- 4.3 Career Decision-Making - Objectives include students researching education levels, credentialing requirements, employment trends in health professions, and distinguishing the differences among careers within a health science pathway.
- 4.4 Employability Preparation - Objectives include students developing components of a personal portfolio and identifying strategies for pursuing employment.
Standard 5: Legal Responsibilities
The purpose of the Legal Responsibilities Standard is for students to describe legal responsibilities, limitations, and implications on healthcare worker actions.
There are two sub-categories in the Legal Responsibilities standard:
- 5.1 Legal Responsibilities and Implications - Objectives include students analyzing legal responsibilities and criminal and civil law implications.
- 5.2 Legal Practices - Objectives include applying standards for health information safety, privacy, and confidentiality.
Standard 6: Ethics
The purpose of the Ethics Standard is for students to understand accepted ethical practices concerning cultural, social, and ethnic differences within the healthcare environment.
There are two sub-categories in the Ethics standard:
- 6.1 Ethical Practice - Objectives include differentiating between ethical and legal issues impacting healthcare.
- 6.2 Cultural, Social, and Ethnic Diversity - Objectives include students demonstrating respectful and empathetic treatment of all patients/clients.
Standard 7: Safety Practices
The purpose of the Safety Practices Standard is for students to identify existing and potential hazards to clients, co-workers, and themselves while employing safe work practices and following health and safety policies and procedures to prevent injury and illness.
There are five sub-categories in the Safety Practices standard:
- 7.1 Infection Control - Objectives include explaining principles of infection transmission, including pathogens and microorganisms.
- 7.2 Personal Safety - Objectives include applying personal safety procedures based on Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and Centers for Disease Control (CDC) regulations and demonstrating principles of body mechanics during patient care.
- 7.3 Environmental Safety - Objectives include students applying safety techniques in the work environment, including ergonomics, safe operation of equipment, and patient/client/employee safety measures.
- 7.4 Common Safety Hazards - Objectives include students to comply with all safety standards related to occupational exposure to hazardous chemicals standard (safety data sheets [SDS]).
- 7.5 Emergency Procedures and Protocols - Objectives include applying basic emergency response principles in natural disasters and other emergencies (safe location, contact emergency personnel, follow facility protocols).
Standard 8: Teamwork
The purpose of the Teamwork Standard is for students to identify individual members’ roles and responsibilities as part of the healthcare team.
There are two sub-categories in the Teamwork standard:
- 8.1 Healthcare Teams - Objectives include evaluating the roles and responsibilities of healthcare team members and identifying effective teams’ characteristics.
- 8.2 Team Member Participation - Objectives include students recognizing methods for building positive team relationships and analyzing the attributes of an effective leader.
Standard 9: Health Maintenance Practices
The purpose of the Health Maintenance Practices Standard is for students to differentiate between wellness and disease while promoting disease prevention and modeling healthy behaviors.
There are two sub-categories in the Health Maintenance Practices standard:
- 9.1 Healthy Behaviors - Objectives include promoting wellness behaviors and investigating complementary and alternative health practices related to wellness and disease prevention.
- 9.2 Healthcare Across the Lifespan - Objectives include discussing physical, mental, social, and behavioral development and its impact on healthcare.
Standard 10: Technical Skills
The purpose of the Technical Skills Standard is for students to apply and demonstrate technical skills and knowledge common to health career specialties.
There is one sub-category in this standard:
- 10.1 Technical Skills - Objectives include demonstrating procedures for measuring and recording vital signs, including the normal ranges.
Standard 11: Information Technology in Healthcare
The purpose of Information Technology in Healthcare Standard is for students to apply information technology practices common across health professions.
There is one sub-category:
- 11.1 Key Principles, Components, and Practices of Health Information Systems (HIS) - Objectives include students identifying components of an electronic health record (EHR) and/or electronic medical record (EMR) and creating electronic documentation that reflects timeliness and completeness and accuracy.
How to Teach a Curriculum Based on the National Health Science Standards
Now that you know the 11 foundation standards, you need to find a curriculum to teach the classes and prepare your students for exam success.
While some teachers create their own curriculum by cobbling together a variety of resources, doing so can take a lot of time and energy (which you probably don't have to spare).
That’s why we created HealthCenter21.
As members of NCHSE Publishers Coalition, our curriculum was developed in accordance with the National Health Science Standards (NHSS).
Because of this, thousands of teachers use HealthCenter21 to meet NCHSE's standards and teach classes, while saving time and increasing student engagement.
When the standards change, we review HealthCenter21 and make any necessary updates to ensure your students receive the most up-to-date information when it comes to the healthcare industry.
Teachers like you also use HealthCenter21 to prepare students for the NCHSE End of Course Assessment based on the NHSS.
Download the guide to see how our curriculum with the NCHSE National Health Science Assessment, and see how it can help build your health science curriculum:

