What Is the NREMT EMR Certification?
The National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) emergency medical responder (EMR) certification evaluates a student’s proficiency in the skills and knowledge needed to respond to emergency calls, assist those who need medical attention, and perform basic lifesaving procedures.
They also assist emergency medical service (EMS) personnel such as emergency medical technicians and paramedics.
In addition, EMRs don’t necessarily have to be dedicated medical professionals. Many police officers, firefighters, and even park rangers are trained EMRs since they may be the first emergency personnel to respond to a call.
That makes earning emergency medical responder certification critical to being part of an EMS response team!
So how can you help your students pass the NREMT EMR exam to become EMR certified?
On this page, you’ll learn the details of what’s on the NREMT EMR exam and how to prepare students for EMR testing.
First, let’s discuss the NREMT since they provide the certification!
What Is the NREMT?

The NREMT is a non-profit organization considered to be “the nation’s emergency medical services certification organization.”
The NREMT’s mission is to protect the public by ensuring EMS professionals can effectively work in the field.
To accomplish this, the NREMT has developed a first responder certification test for four EMS professions, including the National EMR Certification!
Now that you know a little bit about the NREMT, let’s get into the details of the EMR certification!
How Is the NREMT Emergency Medical Responder Certification Exam Structured?

The NREMT EMR exam is made up of a cognitive exam and psychomotor exam.
The cognitive exam is a computer-based test that measures a student’s knowledge of the National EMS Educational Standards laid out by the federal government.
Exams could contain anywhere from 90 to 110 questions, including several potential unscored “pilot questions” the NREMT uses to gather data.
These questions fall under five content areas found on the National EMS Educational Standards:
- Airway, Respiration and Ventilation
- Medicine
- Cardiology and Resuscitation
- Trauma
- Special Patient Populations
- EMS Operations
Each content area is further organized into “sections” and “competencies:”
- “Sections” are the major topics that further elaborate on the overarching knowledge area
- “Competencies” are the individual concepts and skills within each section
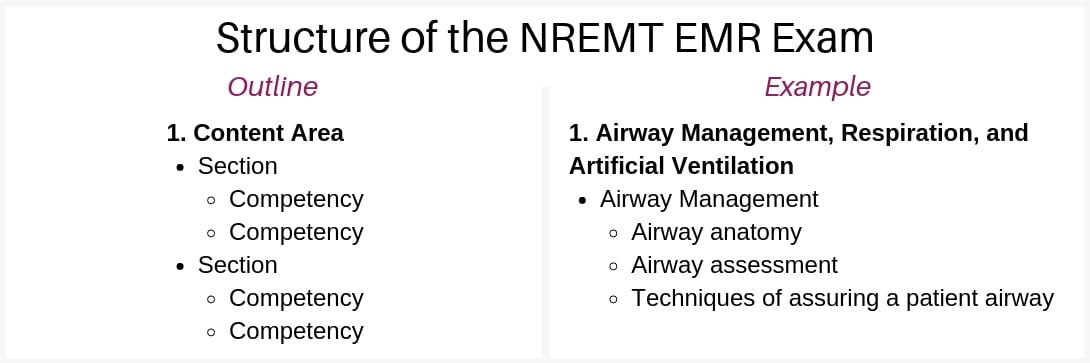
This is what you can expect from each section of the cognitive EMR test.
1. Airway Management, Respiration, and Ventilation
The Airway, Respiration, and Ventilation content area measures a student’s understanding of human respiratory issues.
This area includes 11 competencies across three sections:
- Airway Management
- Respiration
- Artificial Ventilation
These competencies relate to airway assessment, supplemental oxygen therapy, and different types of artificial ventilation.
Overall, it’s crucial for an EMR to have the knowledge and skills necessary to keep a patient breathing while additional EMS workers respond to the scene.
2. Medicine
The Medicine content area evaluates a student’s ability to recognize and manage threats to a patient’s life during a medical emergency when waiting for assistance from other EMS providers.
This area includes 22 competencies across 14 sections:
- Medical Overview
- Neurology
- Abdominal and Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Endocrine Disorders
- Psychiatric or Behavioral Emergencies
- Cardiovascular
- Toxicology
- Respiratory
- Genitourinary/Renal
- Disorders of the Eyes, Ears, Nose, and Throat
- Hematology
- Non-Traumatic Musculoskeletal Disorders
The competencies revolve around an EMR’s ability to recognize medical incidents such as cardiac arrest, diabetic emergencies, anaphylactic reactions, and seizures.
Because EMRs are often the first people on scene during potential medical emergencies, they’re the first medical professionals to evaluate a patient’s status and determine the proper short-term treatment.
3. Shock and Resuscitation
The Shock and Resuscitation content area is one of the simplest portions of the EMR certification.
This content area covers six competencies across two sections:
- Shock
- Resuscitation from Cardiac Arrest
Though this content area is short, it covers one of the most important roles of an EMR.
Recognizing and managing these life-threatening emergencies makes a huge difference when every second counts.
4. Trauma
The Trauma content area evaluates students on recognizing and managing life-threatening trauma.
This area includes 26 competencies across 11 sections:
- Trauma Overview
- Bleeding
- Chest Trauma
- Nervous System Trauma
- Abdominal and Genitourinary Trauma
- Orthopedic Trauma
- Soft Tissue Trauma
- Head, Facial, Neck, and Spine Trauma
- Special Considerations in Trauma
- Environmental Emergencies
- Multi-System Trauma
Even though an EMR is not responsible for the long-term treatment of an acutely injured patient, their initial assessment of someone’s needs and management of the trauma is essential to a victim’s survival.
Lacerations, blunt force, burns, and more can all constitute some degree of trauma. Students must know the tell-tale signs of these injuries if they’re going to successfully keep someone alive until they can be transported to a hospital.
5. Special Patient Populations
The Special Patient Populations content area tests a student’s ability to recognize and manage individuals with special considerations.
This area includes six competencies across six sections:
- Gynecology
- Obstetrics
- Neonatal Care
- Pediatrics
- Geriatrics
- Patients with Special Challenges
Age is perhaps the most common factor that impacts an EMR’s short-term treatment options.
Some emergencies (such as airway obstruction) are managed differently in pediatric patients than adult patients.
It’s also important for EMRs to practice special considerations for pregnant women and those who may have diagnosed behavioral challenges.
6. EMS Operations
EMS Operations tests a student’s knowledge of the operational roles and responsibilities among emergency medical service providers.
This area has 11 competencies across seven sections:
- Emergency Response Vehicles
- Rescue Operations
- Incident Management
- Multiple Casualty Incidents
- Air Medical
- Hazardous Materials
- Mass Casualty Incidents due to Terrorism and Disaster
These include responsibilities like emergency response, triage principles, and the risks of operating on the scene of a disaster.
Having knowledge of these roles and responsibilities helps every EMR work more effectively with other EMS providers to maintain a safe environment for everyone involved.
Now that you know the NREMT categories for the cognitive exam, let's take a closer look at the requirements for the EMR psychomotor exam.
The NREMT EMR Psychomotor Exam
After passing the cognitive exam, students must take the psychomotor exam to earn their emergency medical responder certification.
This section of the test is a hands-on skills assessment of common incidents an EMR may encounter in the field.
Surprisingly, this exam is not administered by the NREMT.
Instead, the state EMS office or an affiliated training institution provides an instructor to evaluate the psychomotor exam.
The NREMT has example performance checklists to help students learn what to expect from the psychomotor exam, including:
- Trauma assessment and management
- Medical emergency assessment and management
- BVM ventilation of an apneic adult patient
- Oxygen administration by non-rebreather mask
- Cardiac arrest management
However, the NREMT notes that the performance checklists used during the actual exam may differ, depending on the person’s local EMS office.
Once a student completes their psychomotor exam, they receive their unofficial results of pass / fail instantly.
The official exam results are posted on their NREMT account within four weeks. If they’ve passed, they are officially certified to work as an EMR!
So, now that you know the details of the NREMT EMR certification, there’s one last question -- how do you prepare your students for success?
How Do You Prepare Students for the NREMT EMR Certification Exam?
When you want to help students earn their emergency medical responder certification, you would ideally want official EMR test prep materials from the certification provider!
Unfortunately, the NREMT doesn’t provide an official study guide. Still, you can find dozens of unofficial options online.
Because these materials don’t come from the NREMT, they could miss important information that students need to know.
On top of that, exclusively teaching to the test can hurt your students’ long-term information retention! If you teach an entire class according to a single certification exam, you’ll also miss important foundational information which may not be on a test, but still essential for EMRs to know.
That’s why it’s smart to take a two-step approach when preparing students for the NREMT EMR exam:
- Teach your EMR curriculum
- Supplement with test prep materials
Start by teaching the foundational skills and concepts found on the National EMS Educational Standards.
Those standards include the detailed competencies found on the exam, plus additional information every EMR must know for a successful career.
It’s also important to discuss your own professional experience as an EMS provider to show real-world context for EMRs.
In addition, it’s smart to incorporate soft skills like communication and professionalism to help your students hone their interpersonal skills for working with patients and colleagues.
Near the end of your semester, throw in a NREMT EMR practice test or two and add additional study materials to see how ready your students are for exam day.
This two-step approach will help you teach the knowledge and skills needed for success on the NREMT EMR exam and in their future careers!
To make this process work, you need to seamlessly tie all of the pieces together in your classroom.
Some teachers do this by building their own EMR curriculum from scratch. This is an excellent way to provide a customized learning experience for your students. But creating lessons, activities, and assessments all on your own could take an entire summer of planning (or longer)!
That’s why dozens of EMR instructors have implemented a comprehensive curriculum system to do the heavy lifting when it comes to planning and preparing students for the NREMT EMR exam!
Prepare Students for the NREMT EMR Exam with AES
EMR instructors across the United States use HealthCenter21 from AES as a primary instructional resource to teach concepts and skills found on the NREMT EMR exam.
The AES curriculum system streamlines busy work like planning lessons so you can focus on helping students prepare for their careers as emergency medical responders.
It’s here to help take your students from zero to certified by providing up-to-date lessons, engaging activities, scenario-based learning, and automatically-graded assessments.
To top it all off, HealthCenter21 is aligned to the National EMR Educational Standards that the exam is based on. With AES, you can confidently prepare your students for the National Registry Exam.
Want to learn how AES can help you prepare your students? Click below to download your NREMT EMR certification success guide!

